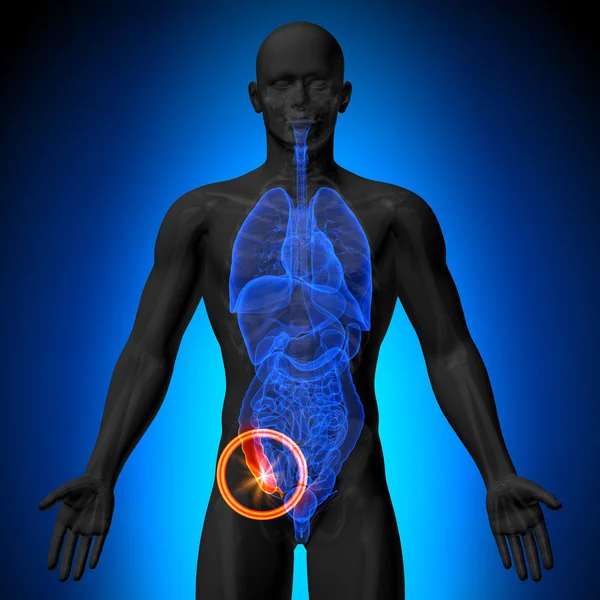
The appendix is a small, tubular organ attached to the cecum, which is the pouch-like beginning of the large intestine. Positioned in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, just below where the small intestine joins the large intestine, it typically measures approximately 3 to 4 inches in length. The appendix is characterized by its slender, finger-like shape and has a narrow opening called the appendiceal orifice through which it connects to the cecum. Despite its seemingly innocuous appearance, the appendix has garnered significant attention due to its historical classification as a vestigial organ—thought to be a remnant of evolutionary development without any clear function in modern humans.

What is the appendix, and where is it located?
The appendix is a thin, finger-like pouch located in the lower right part of the abdomen, where the small intestine meets the large intestine. It is approximately 3 to 4 inches long and is attached to the cecum, which is the initial part of the large intestine.
Historical Perspectives on the Appendix: Once Thought Useless
Historically, the appendix was considered a vestigial organ—meaning it had lost its original function through evolution. Like other structures such as wisdom teeth or the tailbone, it was believed to serve no significant purpose in modern humans.
Recent Discoveries and Changing Views
Recent research has challenged the view that the appendix is functionless. Studies have shown that it contains a considerable amount of lymphoid tissue, which plays a crucial role in immune function. This tissue helps regulate gut flora, the community of microorganisms in the intestines, and may contribute to immune responses, particularly during early stages of life.
Appendicitis: A Common Problem
Despite its potential benefits, the appendix is prone to inflammation, a condition known as appendicitis. Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, often due to the accumulation of fecal matter, infections, or swelling of lymphatic tissue. This blockage can lead to inflammation, bacterial overgrowth, and potentially life-threatening complications if the appendix ruptures.
Treatment and Removal
The standard treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix, a procedure called an appendectomy. This surgery is generally effective in resolving appendicitis and preventing further complications. While the appendix may contribute to immune function, most individuals can lead healthy lives without it after removal.
The Debate Continues: Functions and Evolutionary Significance
Despite advances in understanding, many questions about the appendix remain unanswered. Scientists continue to investigate its precise functions, evolutionary origins, and potential long-term impacts of its removal on health. Some hypotheses suggest the appendix may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria, aiding in recovery after gastrointestinal infections.
Looking Ahead: Future Research Directions
Future research aims to delve deeper into the role of the appendix in human biology. Ongoing studies may uncover additional functions related to immune modulation, clarify its evolutionary development, and explore links between appendicitis and broader aspects of human health. Understanding these aspects could provide valuable insights into how the appendix contributes to overall health and disease prevention.
Read more about Appendix on https://www.britannica.com/science/appendix
Conclusion
In conclusion, while once considered a functionally obsolete organ, current research suggests the appendix may play significant roles in immune regulation and gut health. Its propensity for causing appendicitis underscores its ongoing relevance in medical research and clinical practice. As scientific understanding advances, so too does our appreciation of this small yet potentially crucial organ in the intricate workings of human physiology. Continued research promises to unlock more secrets about the appendix, potentially reshaping our understanding of its importance in human health.